May / 07
Rule includes at least one "precondition" and one "postcondition".
*precondition evaluates a data point
*postcondition giving hypothesis output fot the data point
ex) if a fruit is red and circular, it is an apple.
precondition : "red and circular"
postcondition: "it is an apple"
rule: if a fruit is red and circular, it is an apple.
There are two rules which are Classification rule, and Association rule
-> Classification rule: classify a data point to a typical class.
-> Association rule: find a relationships between data points.
1 Rule
- 1.1 Conditional relation ship: if a precondition of rule a retuns "true" for a typical data point, the data point will do postcondition of the rule.
- 1.2 Sequential evaluation of rules: if a data returns "true" and be applied postcondition, the data will not be evaluated from next condition ( there are multiple conditions in a model)
- 1.2.1 set of rules evaluate a data point one by one.
- 1.2.2 if a data point is returns "false" from rule A, the data point will be evaluated by rule B.
- 1.3 Variable: it is possible to a condition includes a variable
ex) if a fruit is "X", it is "Y" : X can be red, yellow, green ...., Y can be apple, banana, melon.
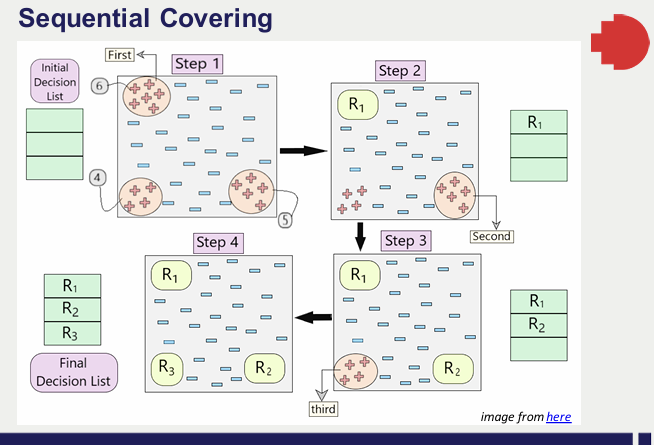
2. Sequential covering (rule-based machine learning algorithm): it is one of the algorithms that use classification rule
- 1. the model create a rule that includes as much data as the postcondition returns true.
- 2. apply the rule to the dataset
- 3. classify the data points based on the rule
- 4. except the data points that were classified in step 3
- 5. return to 1 till all data points are classified.
3. Apriori algorighm (rule-based machine learning algorithm): it is one of the algorithms that use association rule. Normally it is used in market baket anlaysis.
ex) to find the relationships between the items that are sold by consumers
- Key factors)
- Support : the percentage of a certain relationship
ex) the dataset represnts the set of items purchased by customers in a specific market. If a relation is found which is that normally when customer purchase bread, butter is included in the set of items.
The support of relation between bread and butter
= (num of purchase that includes both bread and butter) / total num of puchase - Confidence: if A is existing in a data point, the percentage of B is also included in the data point.
ex) if a puchase includes bread, the percentage of butter is also included in the purchase.
confidence = (the num of purchase includes both bread and butter) / (total num of purchase) - Lift: it is key metric used to evaluate the strength of an association rule. if the lift value is greater than 1, it is considred that there is a positive association between the two items.
ex) finds association between bread and butter.
Lift = confidence of bread and butter / (the num of purchase which includes butter / num of total purchase)
- Support : the percentage of a certain relationship
- Aprior algorithm operation
- find most frequent item
- find the one more item have a relationship with the item (set of item)
- if the support of relationship(association) is greater than minimum support values that the user decide, expand the set of items.
* The mean of 1,2,3 is create a rule* => create rule and make it increasingly more specific hypotheses
